Bcs Class Iv
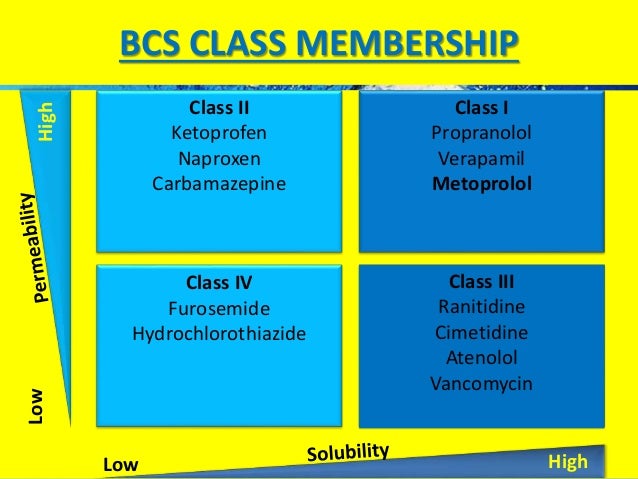
The BDDCS classification indicated that 59 drugs are class I, 51 class II, 42 class III, and 12 drugs out of the 164 are class IV compounds. The BCS classification based on metoprolol as the reference compound indicated a total of 42, 54, 57, and 11 drugs as class I, II, III, and IV, respectively. On drug permeability.[4] The BCS guidance takes into account three major factors, dissolution, solubility, and intestinal permeability, which govern the rate.
Bioavailability enhancement techniques for BCS Class II and Class IV drugs 3 rd International Conference and Exhibition on Biowaivers, Biologics & Biosimilars Jithan Venkata Aukunuru Keynote: DOI: Abstract Bioavailability is the rate and extent (amount) of absorption of unchanged drug from its dosage form. It is one of the important parameter to achieve desired concentration of drug in systemic circulation for pharmacological response to be shown. A drug with poor bioavailability is one with poor aqueous solubility, slow dissolution rate in biological fluids, poor stability of dissolved drug at physiological pH, poor permeation through biomembrane, extensive presystemic metabol ism. From BCS candidates, class II and class IV drugs have solubility and permeability problems because of which their bioavailability is poor. Poorly water soluble drugs often require high doses in order to reach therapeutic plasma concentrations after oral administration.
Low aqueous solubility is the major problem encountered with formulation development of new chemical entities. Any drug to be absorbed must be present in the form of an aqueous solution at the site of absorption. This presentation focuses on the various techniques used for the improvement of the Bioavailability of BCS class II and class IV drugs including size reduction, solubilising excipients, colloidal drug delivery systems, pH adjustment, solid dispersion, complexation, cosolvency, micellar solubilisation, hydrotropy etc.
Biography Jithan Venkata Aukunuru is presently a Professor and Principal at Mother Teresa College of Pharmacy (Affiliated to Osmania University), Hyderabad. Jithan is a recipient of several awards and medals in his entire academic career. His research interests include Novel Oral Delivery Technologies; Exploratory Pharmaceutics; IVIVC; Implants; Nanosuspensions; Microspheres; Proliposomes; Prodrugs; Colon Drug Delivery; Nanotechnology; Chronotherapeutics; Novel Transdermal Delivery Methods; Exploratory Pharmaceutics; Drug Metabolism; Pharmacology (Retinal and Liver Disorders); Solubility Enhancement. He was awarded Ph.D in 2002 from University of Nebraska Medical Sciences, USA, in Pharmaceutical Sciences. For his PhD, he worked on retinal delivery of small and macromolecules. He is a fellow of Association for Biotechnology & Pharmacy and an active member of APP, APTI, IPA and IPGA. .
Bcs Class 1 Drugs
Utorrent free music downloads mp3. Bioavailability enhancement study of BCS class IV drug: Snedds approach 4 th International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems Bhupendra Prajapati Accepted Abstracts: DOI: Abstract The purpose of present study is to formulate SNEDDS of BCS Class-IV (Exemestane HCl) to investigate its potential oral drug delivery system by improving its bioavailability. Preformulation study was done for selection of oils, surfactants & co-surfactants. Based on the solubility studies, Caprol microexpress and Labrafac as oil phase, Tween 80 as a surfactant and Triacetin as a co-surfactant were selected. Phase studies were performed using different ratio like (1:1, 1:2, 1:3, 2:1, 3:1) [oil: (surfactant/co-surfactant)]. Pseudo ternary phase diagram were prepared, Tween 80: triacetin (1:2) and (1:3) ratio showed the highest area for the preparation for the nanoemulsion.
All formulations were evaluated for the visual assessment, optical clarity, particle size, drug content, viscosity, in vitro release study. From vitro characterization results, three formulations were selected as potential formulation for in vitro cytotoxicity screening and in vivo pharmacokinetic study. EX1 showed particle size (29.56 nm), Polydispersity index (0.523), Zeta potential (-40.3), & drug release after 120 min. Was 99.589?1.85% EX2 showed particle size (37.65 nm ), Polydispersity index (0.835), Zeta potential (-30.3), & drug release after 120 min was 99.17?1.81% EX3 showed particle size (44.73 nm), Polydispersity index (0.679), Zeta potential (-15.7), & drug release after 120 min was 98.172?1.29% due to its low particle size and excellent stability.